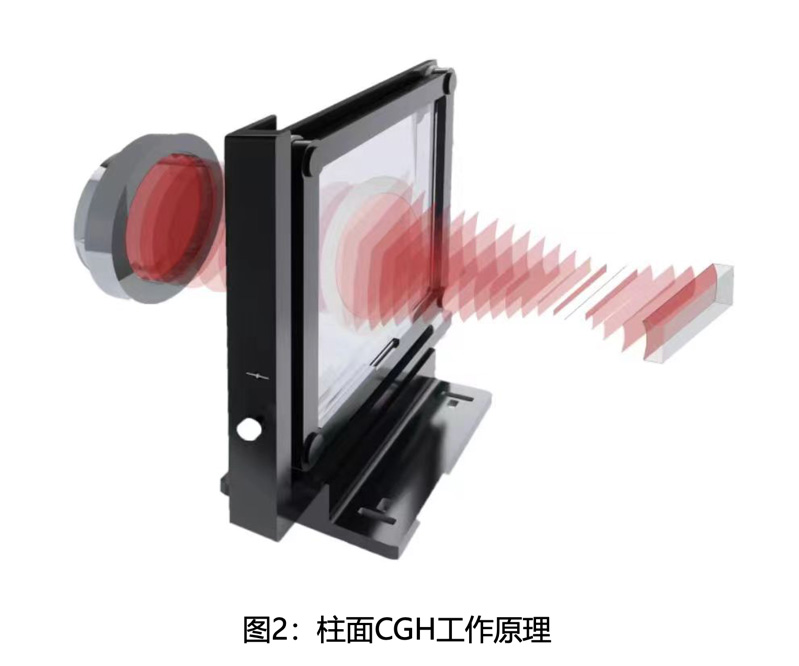
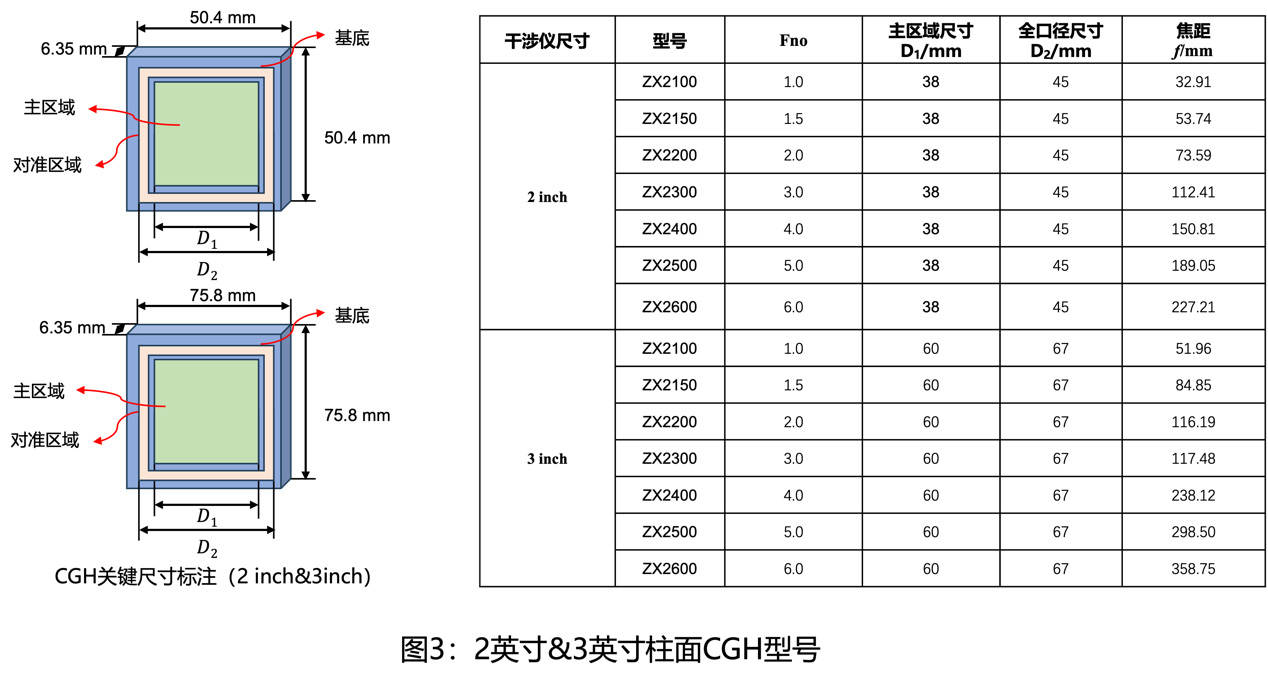
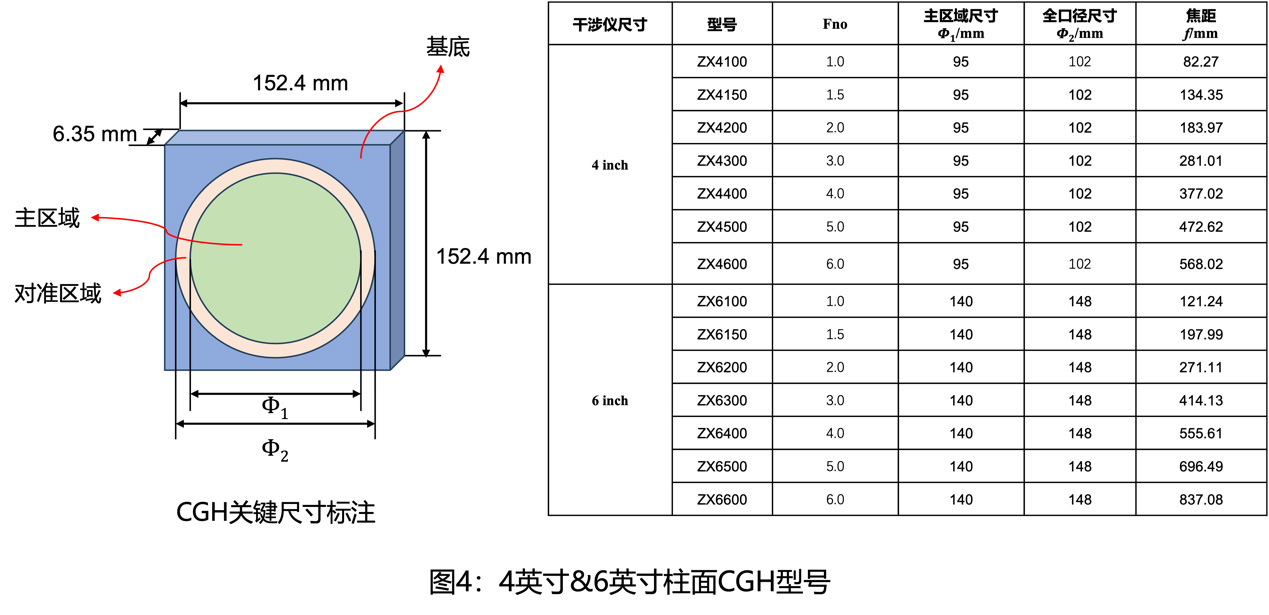
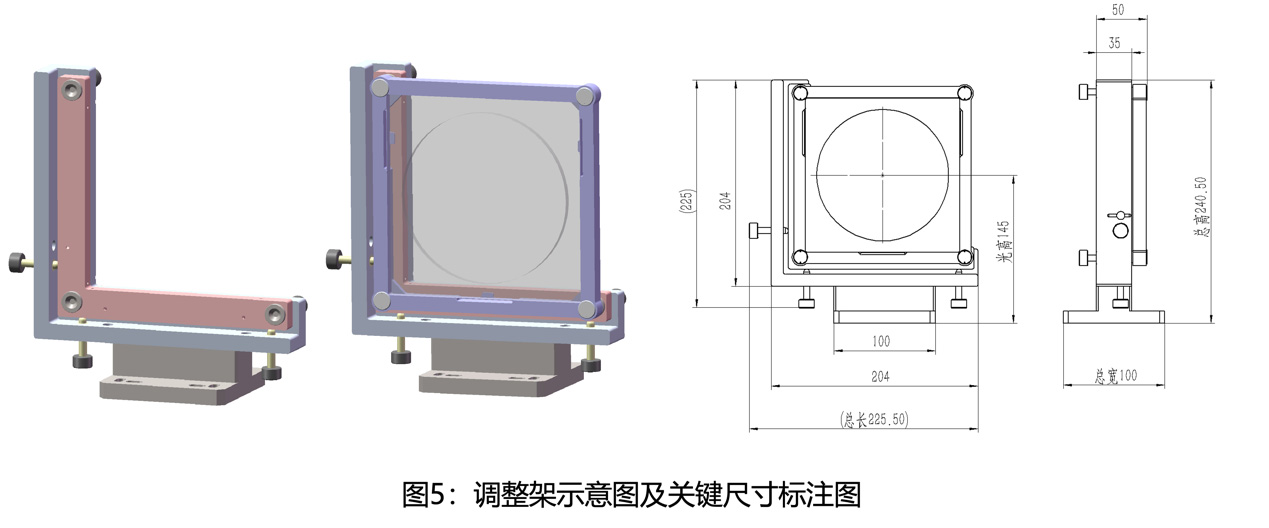
CN
Home
About Us

About Us
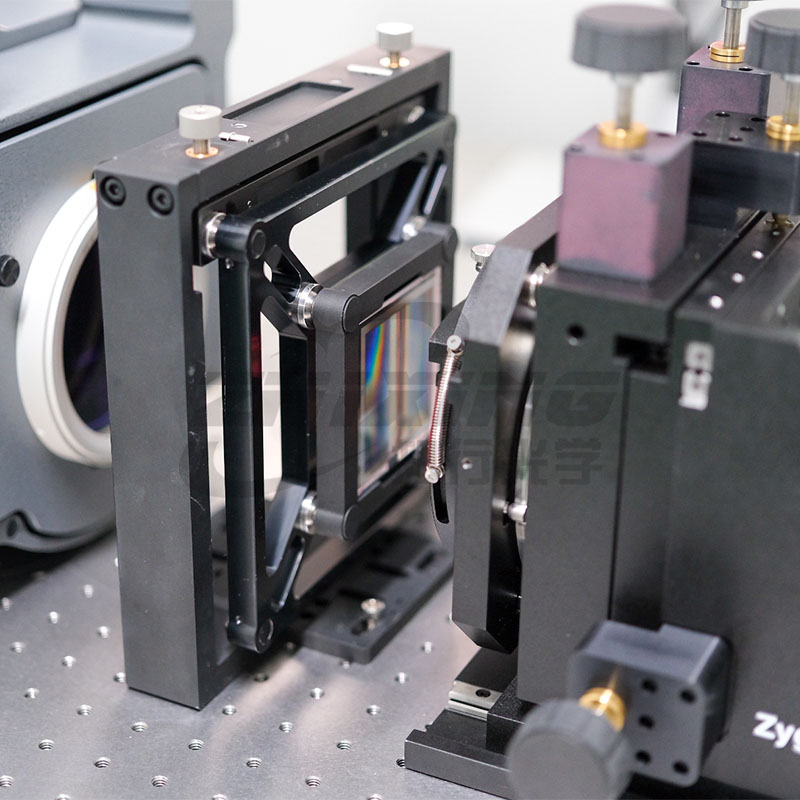
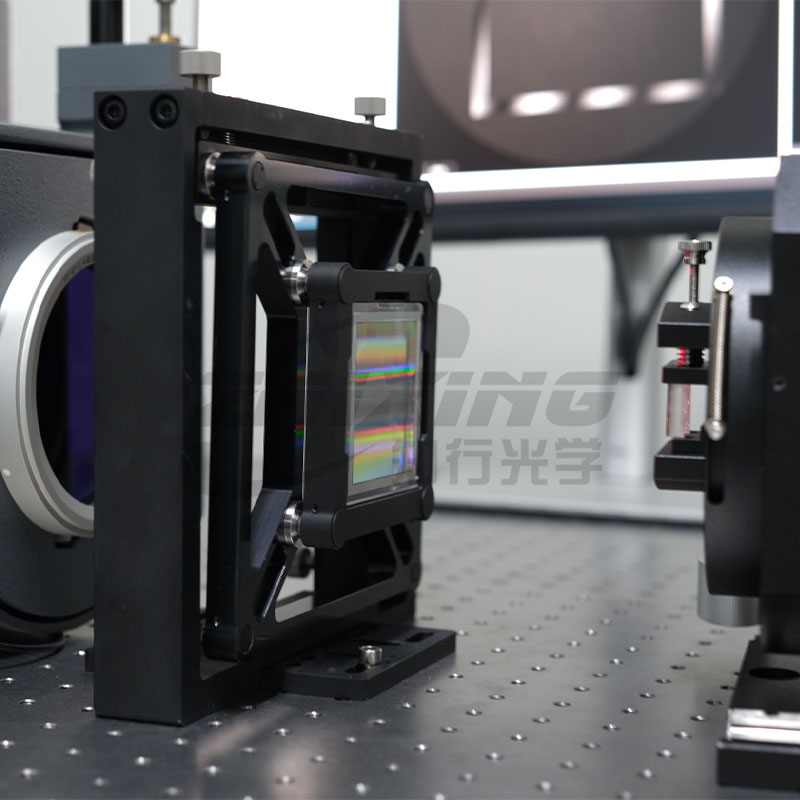
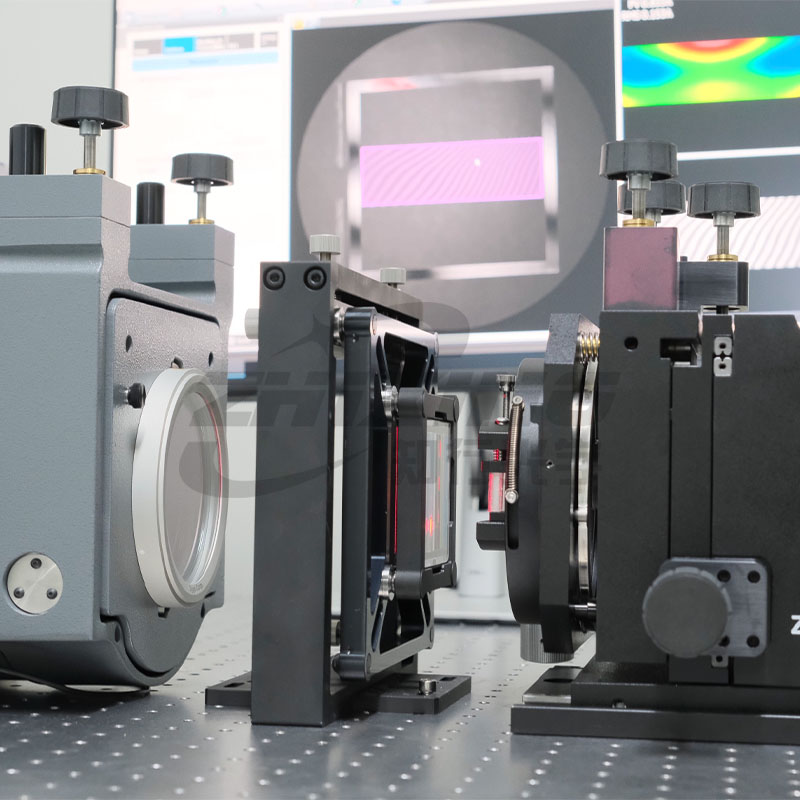
Ningbo Zhixing Optical Technology Co., Ltd. is a technology-based enterprise specializing in the research and development of optical devices
Products

Products
Ningbo Zhixing Optical Technology Co., Ltd. is a technology-based enterprise specializing in the research and development of optical devices
Contact Us

Contact Us
Ningbo Zhixing Optical Technology Co., Ltd. is a technology-based enterprise specializing in the research and development of optical devices